Mechanical Ventilation Is Key for Today’s Tightly Built Homes
How do you get fresh air in and stale air and cooking odors out in a well-insulated house? Mechanical ventilation is key for today’s tightly built homes. Controlling the quantity and quality of the air in your home is good for your health as well as the health of your home.
Mechanical ventilation improves indoor air quality by providing fresh air and diluting pollutants, controls moisture, prevents inadequate air flow, and doesn’t rely on occupants to open windows.
There are three ways to circulate air:
- Mechanical exhaust systems (local or multi-point)
- Mechanical supply systems
- Balanced mechanical systems (exhaust and supply)
To comply with building codes, new homes are required to have a continuous method of moving air, whether by an exhaust, supply or balanced system. Although not required for renovations and remodeling projects, best business practices dictate that builders and subcontractors try to meet this standard.
Mechanical exhaust systems include kitchen hoods and fans, bathroom fans and/or a common living area exhaust system. Mechanical supply ventilation is sometimes attached to the HVAC system. Balanced systems can also be attached to the existing duct work. There are pros and cons for each system.
Advantages/Disadvantages of Exhaust-Only Ventilation

Kitchen hoods are an example of mechanical exhaust ventilation.
Advantages
- Simple to install and inexpensive
- Can be combined with spot ventilation (e.g. bath fan)
- Negative house pressure lowers condensation risk
Disadvantages
- Source of incoming air is not controlled
- Potential back-drafting of combustion appliances
- Other pollutants, such as radon, may enter the house
- Air not distributed evenly throughout the house (with a single-point system)
Advantages/Disadvantages of Supply-only Ventilation
Advantages
- Inexpensive; can use existing duct systems
- Better distribution of fresh air
- Distributed air can be filtered
- Positive pressure keeps outdoor air pollutants out
Disadvantages
- Uncomfortable drafts of air at the point of intake (not great in cold weather climates)
- Warm moist air is forced into envelope assemblies
- Using air-handler fan results in higher electricity use
- Air-handler limitations on the temperature of intake air
Advantages/Disadvantages of Balanced Ventilation
Here are two methods of balanced mechanical ventilation: HRV – heat recovery ventilation and ERV – Energy Recovery Ventilation. HRV transfers only sensible heat. Sensible heat is heat that you can feel. ERV transfers sensible heat and latent heat. These terms refer to how energy is absorbed in a space. HVAC systems are designed to account for indoor conditions (humans, furnishings, etc.) in a house and fluctuations in outside temperature and conditions.
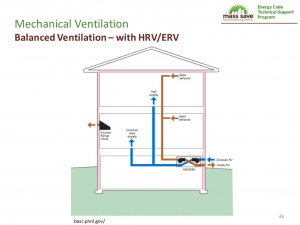
Advantages
- Can recover energy with an HRV or ERV system
- Applicable in all climate zones
- Source of ventilation air known (i.e. fresh air)
- Filtered and tempered outdoor air
- House pressure approximately equal to outside
Disadvantages
- Can be more expensive
- Requires proper planning during the design phase
- Local exhaust still required if not exhausting from bathrooms
The team at Lavallee Systems will guide you through the myriad of product choices and help you determine which ventilation system is best for your home.